Monsoon
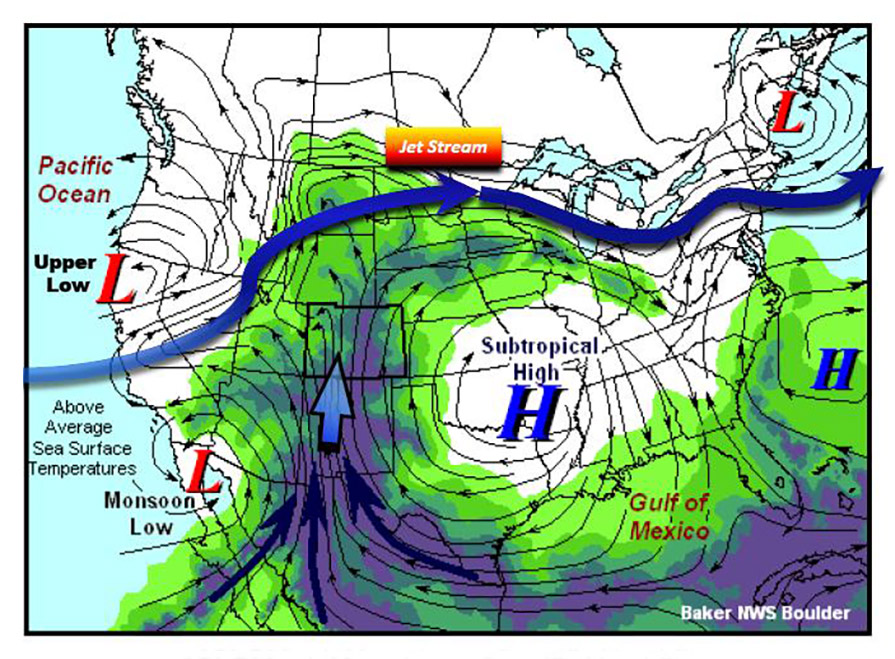
Source: Jeppesen | NWS | NOAA
While most people associate the word ‘monsoon’ with precipitation, the term is actually derived from the Arabic word ‘mausim’, which means season. Traders used it to describe the alternating winds which blow from the northeast during the winter and from the southwest in the summer over the Indian Ocean. The term monsoon refers only to the seasonal shift in the wind direction.
The change in the wind direction is based on two meteorological changes: the seasonal movement of the the Bermuda High and a intense heating over land which leads to rising air in the Mohave Desert.
While the term was originally used to define the circulation over the Indian subcontinent, these circulations exist in locations all over the world. In the United States, the southwestern states are in one of these locations and is commonly referred to as the North American Monsoon. During the summer months, the winds shift from the west to the south and southeast, allowing moisture from the Gulf of California and the Gulf of Mexico to funnel into the area. This moisture rises as it encounters the higher terrain and forms thunderstorms, which can produce high wind and heavy rains. The onset of the North American Monsoon season typically occurs in July and lasts through mid-September..