Agricultural Drought
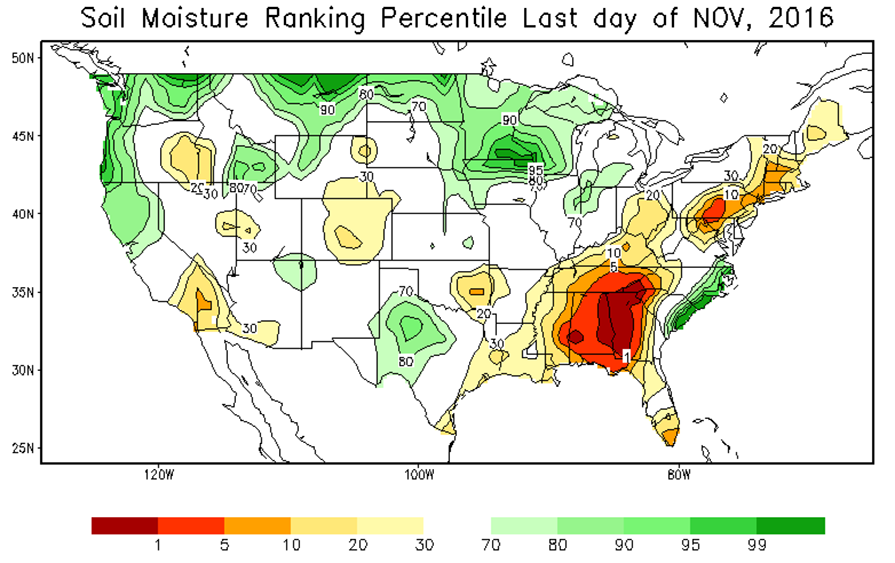
Source: Calculated Soil Moisture Ranking Percentile | NOAA
Agricultural droughts link the characteristics of both meteorological and hydrological droughts. This type of drought illustrates impacts to agriculture; which includes crops, livestock, and forestry. In order to determine if a drought can be classified as an agricultural drought, the following factors are monitored:
- Precipitation shortages
- Increases in evaporation and transpiration
- Topsoil and subsurface moisture deficits
- Reduced groundwater and reservoir levels
Though agricultural droughts are primarily short-term droughts, they can have lasting impacts on the industry and affect irrigated and non-irrigated production areas.
The image from NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center shows the how dry or wet the soil moisture is across the continental United States.