Köppen Climate Classification
Climate covers everything from averages to extremes of different meteorological variables, such as temperature and precipitation. Köppen climate classifications give information about these different variables.
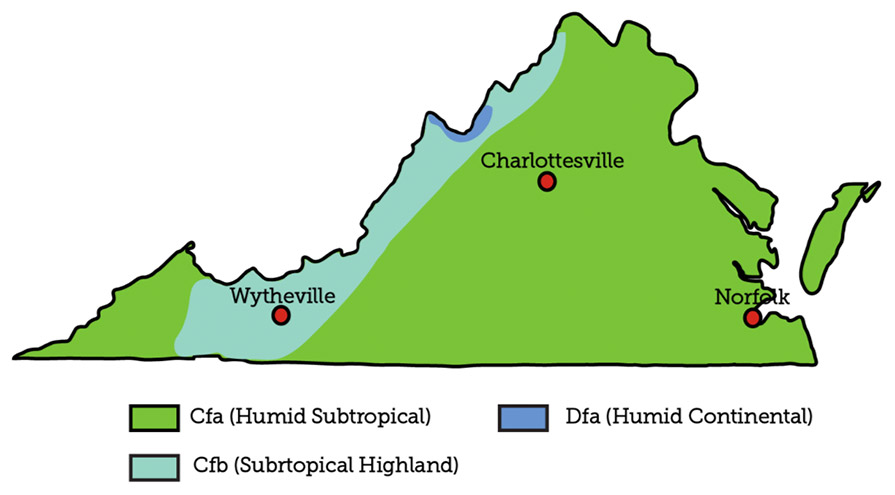
Most of Virginia is categorized as a humid subtropical climate, though portions of the state along the Appalachian Mountains have a subtropical highland climate.
Humid Subtropical: This climate zone has warm-to-hot summers with cold-to-mild winters. The average temperature of the coldest month is below 64°F (17.8°C) and above 27°F (-2.8°C). There is usually no dry season with this classification, and the rainfall is highly variable year-round.
Subtropical Highlands: This climatic zone is a subset of the oceanic climates that exist in elevated portions of the world located within the subtropics. It generally features cool summers and winters, and small shifts in the annual temperature. The higher altitudes mean the climate of these higher altitude regions share similar characteristics to oceanic climates but tend to have drier weather during certain seasons.
Humid Continental: This climate zone has warm-to-hot (humid) summers with cold (sometimes bitterly cold) winters. The average temperature of the warmest month is 71.6°F (22°C). There is usually no dry season with this classification, and the rainfall is evenly distributed throughout the year.
Let’s explore the influences on the climatic zones of Virginia.