Köppen Climate Classifications
Climate covers everything from averages to extremes of different meteorological variables, such as temperature and precipitation. Köppen’s climate classifications give information about these different variables.
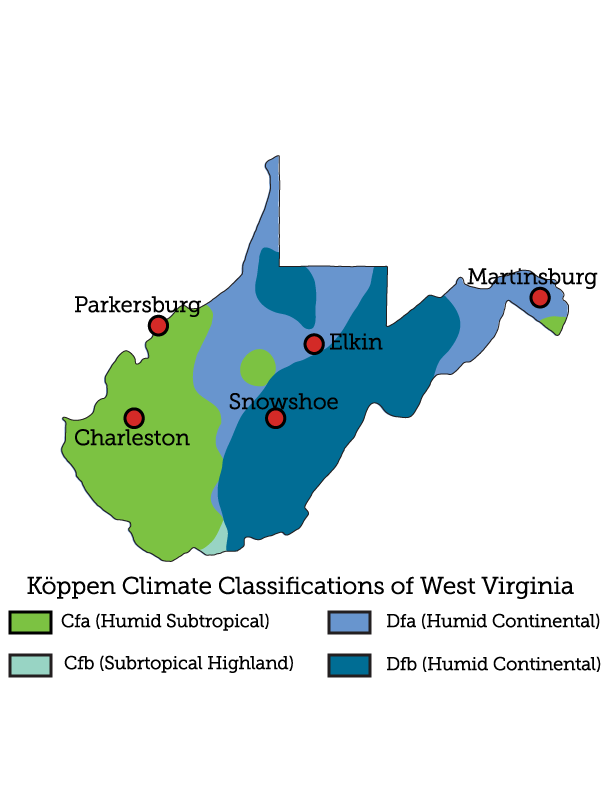
This climate zone has warm-to-hot summers with cold-to-mild winters. The
average temperature of the coldest month is below 64°F (17.8˚C) and above
27°F (-2.8˚C). There is usually no dry season with this classification,
and the rainfall is highly variable year-round.
This climatic zone is a subset of the oceanic climates that exist in
elevated portions of the world located within the subtropics. It generally
features cool summers and winters, and small shifts in the annual
temperature. The higher altitudes mean the climate of these higher
altitude regions share similar characteristics to oceanic climates but
tend to have drier weather during certain seasons.
This climate zone has warm-to-hot (humid) summers with cold (sometimes
bitterly cold) winters. The average temperature of the warmest month is
71.6°F (22˚C). There is usually no dry season with this classification, and
the rainfall is evenly distributed throughout the year.
This climate zone has an average temperature in the warmest month below
72˚F (22 °C) and the average temperatures in the coldest month are generally
far below the 27˚F (−3 °C). Summer high temperatures in this zone typically
average between 70–82 °F (21–28 °C) during the daytime. There is only about
a 3-5 month frost-free period, and heatwaves rarely last over a week.
Because of West Virginia's unique geography and location, its climate is the marked temperature contrast between summer and winter, with four distinct seasons. Let's explore the influences on the climatic zones for West Virginia.