Temperature
- Usually, air is cooler the higher it gets in the atmosphere. But sometimes the opposite happens. This is called a temperature inversion.
- This warm air can act as a lid, trapping the cooler air and smoke at the surface during a fireworks display.
- The smoke can lead to block the view of the fireworks, but can also cause coughing.
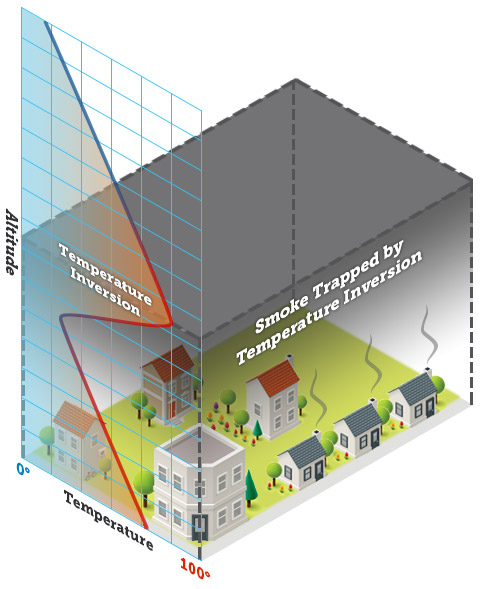
Temperature inversion showing smoke trapped by a layer of warm air.