How Is Heat Measured?
Temperature is the measure of heat energy. However, there are some other indices used to designate risk factors associated with heat and sunlight. Let’s take a look at some of them.
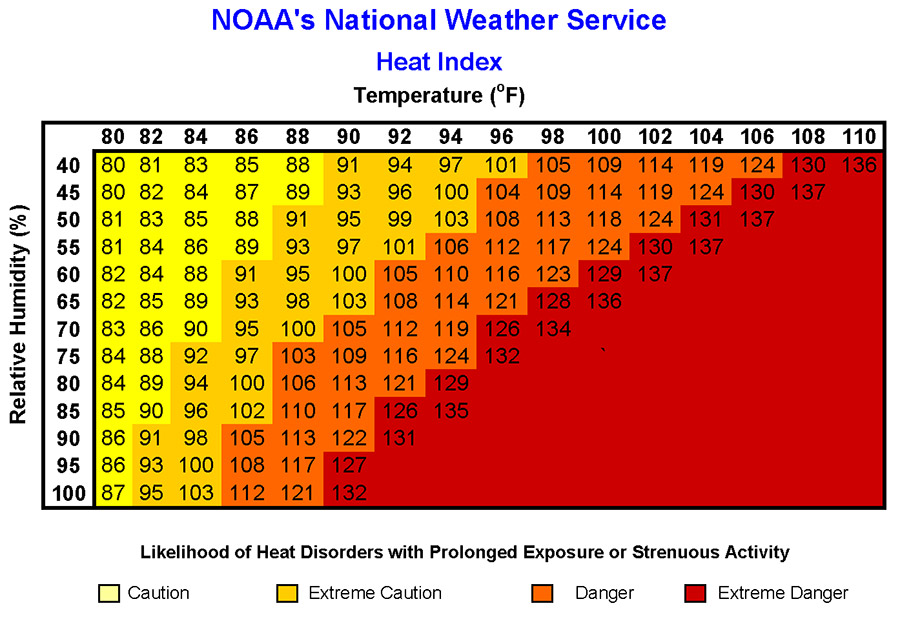
Heat index, also known as apparent temperature, is the measure of how hot it really feels when relative humidity is factored in with the actual air temperature.
Heat index values were devised for shady, light wind conditions. Exposure to full sunshine can increase heat index values by up to 15˚F.
- The Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) is not quite the same as heat index.
- The WBGT is taken in the Sun to account for the intensity and angle of the Sun’s energy striking the Earth.
- It also uses wind measurements to get a more accurate picture of how people respond to hot weather conditions. The colored flags indicate the level of heat stress danger.
| Category | WBGT°F | WBGT°C | Flag Color |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | <= 79.9 | <= 26.6 | White |
| 2 | 80 - 84.9 | 26.7 - 29.3 | Green |
| 3 | 85 - 87.9 | 29.4 - 31.0 | Yellow |
| 4 | 88 - 89.9 | 31.1 - 32.1 | Red |
| 5 | => 90 | => 32.2 | Black |
Source: WeatherSTEM
The Ultra Violet (UV) index is the amount of skin damaging UV radiation expected to reach the earth’s surface at the time when the sun is at the highest point in the sky, known as solar noon.
It ranges on a scale of 0 (nighttime) to 16 (high, tropical elevations with clear skies).
The higher the index the higher dose rate of damaging UV radiation the skin and eyes are exposed to, causing sunburns.
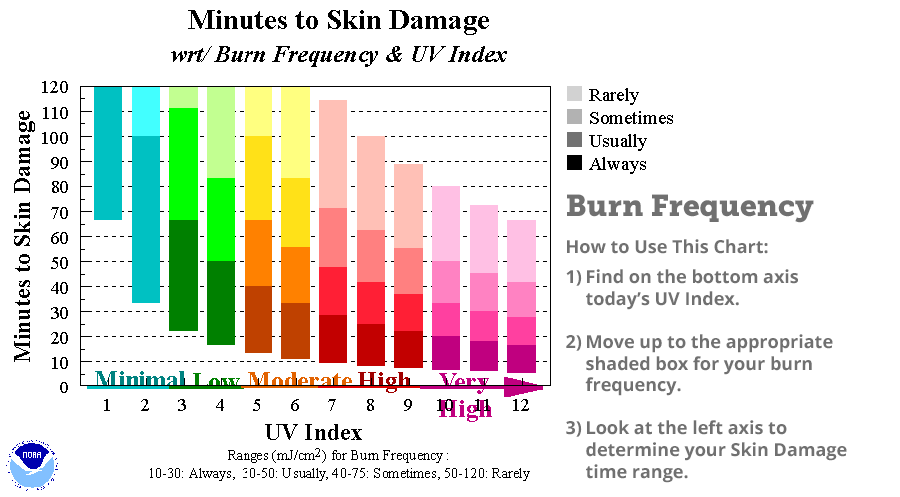
Source: Minutes to Skin Damage | NOAA