Köppen Climate Classifications
Climate covers everything from averages to extremes of different meteorological variables, such as temperature and precipitation. Köppen climate classifications give information about these different variables. Texas has eight unique climatic zones across an area of 268,581 square miles, though they can be categorized by two major climatic types:
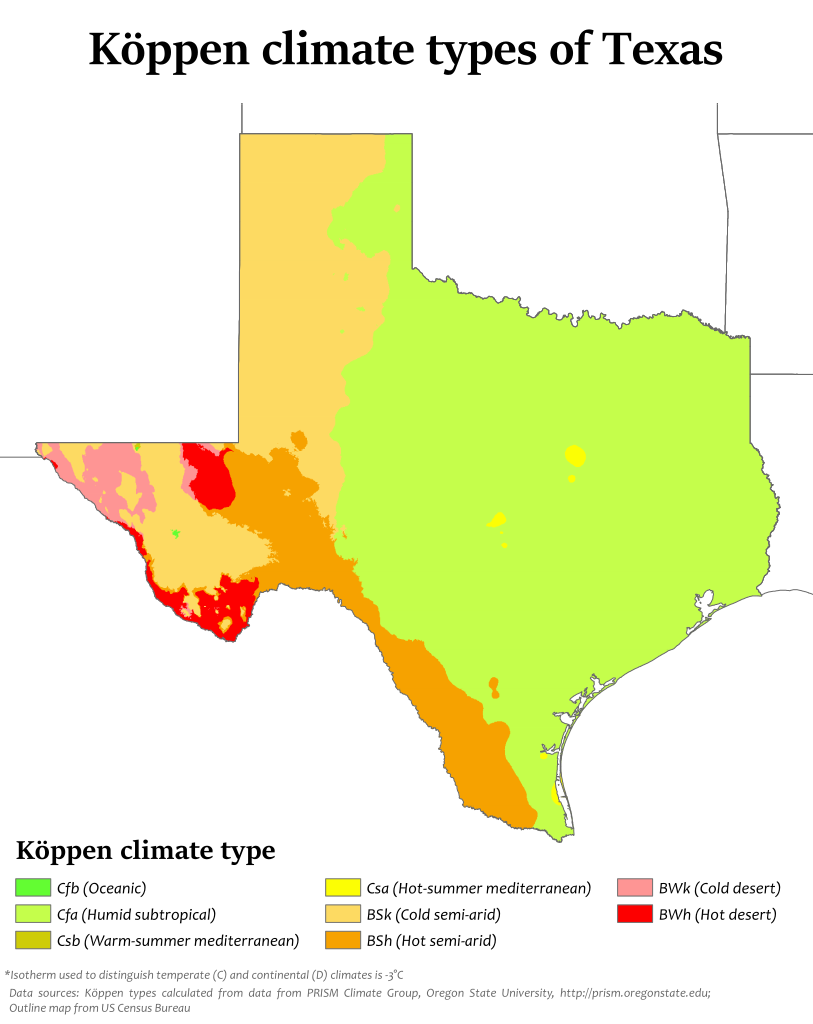
Dry (arid and semiarid) - confined to the Trans-Pecos region of Texas and is characterized by little precipitation, receiving an average annual rainfall total of 16 inches or less.
Temperate - nearly two-thirds of the state falls under this classification, it is known as a modified marine climate, and is caused by the predominant onshore flow of air from the Gulf of Mexico. The climate type is modified by the decrease in moisture the further inland and away from the Gulf.