Standard Variables
Recall that there are 5 standard variables that are measured in the atmosphere. Let’s take a look at how each of these variables is measured.
The average kinetic energy in a sample of air is measured as the air temperature.
This kinetic energy comes from the sun and is transferred between the Earth’s spheres, including the atmosphere.
Temperature is measured with a thermometer and is expressed in either degrees Fahrenheit or degrees Celsius.
Use the converter to see equivalent Fahrenheit and Celcius temperature measurements.
Atmospheric pressure is the force that the atmosphere exerts on the surface of the Earth due to gravity.
Air pressure depends on the density of the air, denser air exerts more pressure than less dense air. Pressure is measured by a barometer and can be expressed in units of:
- millibars (mb)
- atmospheres (atmos)
- Inches of Mercury (in Hg.)
“Standard” atmospheric pressure is 1 atmos, which is equivalent to 1013.25 mb or 29.92 in Hg.
Wind is the horizontal motion of the air; usually due to pressure differences.
Wind can come from all directions. Wind vanes measure the direction from which wind is blowing on a 360˚ compass by tens.
Wind speed is measured by a spinning device called an anemometer.
Wind traveling at 1 mph is also traveling at 0.4 m/s or 0.87 knots.

Image Source: WeatherSTEM
Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air and is important to weather because as it condenses, clouds will form.
There are many ways to represent the measure of moisture in the atmosphere, the most common of which is relative humidity.
Relative humidity is expressed as a percent and is measured with either a hygrometer, or a sling psychrometer.
Precipitation is any water that falls to Earth, including rain, sleet, snow, and hail.
Hail is measured by using a ruler to determine the diameter of hailstones.
Rain and snow are measured with a rain gauge, either automated or manual.
The standard units used for precipitation are:
1 inch = 25.4 mm = 2.54 cm
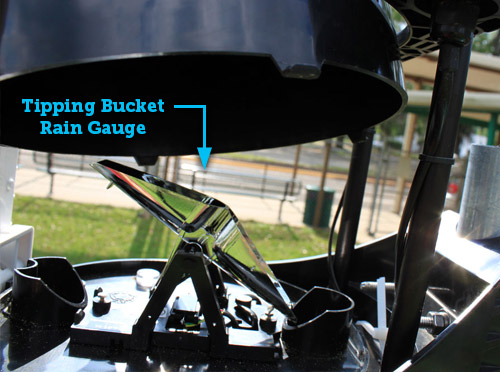
Image Source: WeatherSTEM

