Clouds
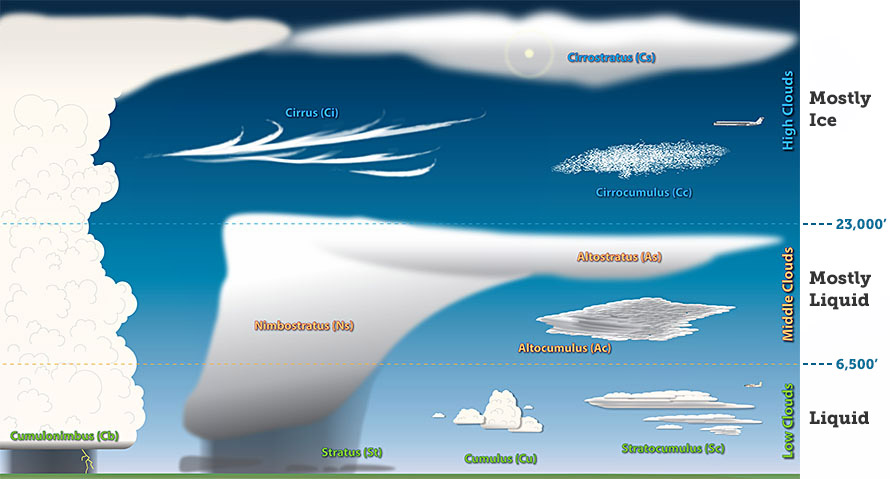
Appearance (texture)
Distance above ground
Other characteristics
Cloud Graphic Source: Clouds | NWS
Cloud Images Sources: Ten Basic Clouds | NWS

Cirrus
Wispy, feathery, and composed entirely of ice crystals. They often are the first sign of an approaching warm front or upper-level jet streak.

Cumulus
More cellular (individual) in nature, have flat bottoms and rounded tops, and grow vertically

Stratus
Uniform and flat, producing a gray layer of cloud cover which may be precipitation-free or may cause periods of light precipitation or drizzle

Cirrostratus
Form more of a widespread, veil-like layer (similar to what stratus clouds do in low levels)

Cirrocumulus
Layered clouds permeated with small cumuliform lumpiness. They also may line up in streets or rows of clouds across the sky denoting localized areas of ascent (cloud axes) and descent (cloud-free channels).

Altostratus
"Strato" type clouds that possess a flat and uniform type texture in the mid levels.

Altocumulus
Exhibit "cumulo" type characteristics (see below) in mid levels, i.e., heap-like clouds with convective elements.

Stratocumulus
Hybrids of layered stratus and cellular cumulus, i.e., individual cloud elements clumped together in a continuous distribution. Stratocumulus also can be thought of as a layer of cloud clumps with thick and thin areas.

Nimbostratus
Generally thick, dense stratus or stratocumulus clouds producing steady rain or snow

Cumulus congestus
A cumulus cloud that exhibits significant vertical development (but is not yet a thunderstorm)

Cumulonimbus
Thunderstorm producing heavy rain. In addition, cloud electrification occurs within cumulonimbus clouds due to many collisions between charged water droplet, graupel (ice-water mix), and ice crystals, resulting in lightning.